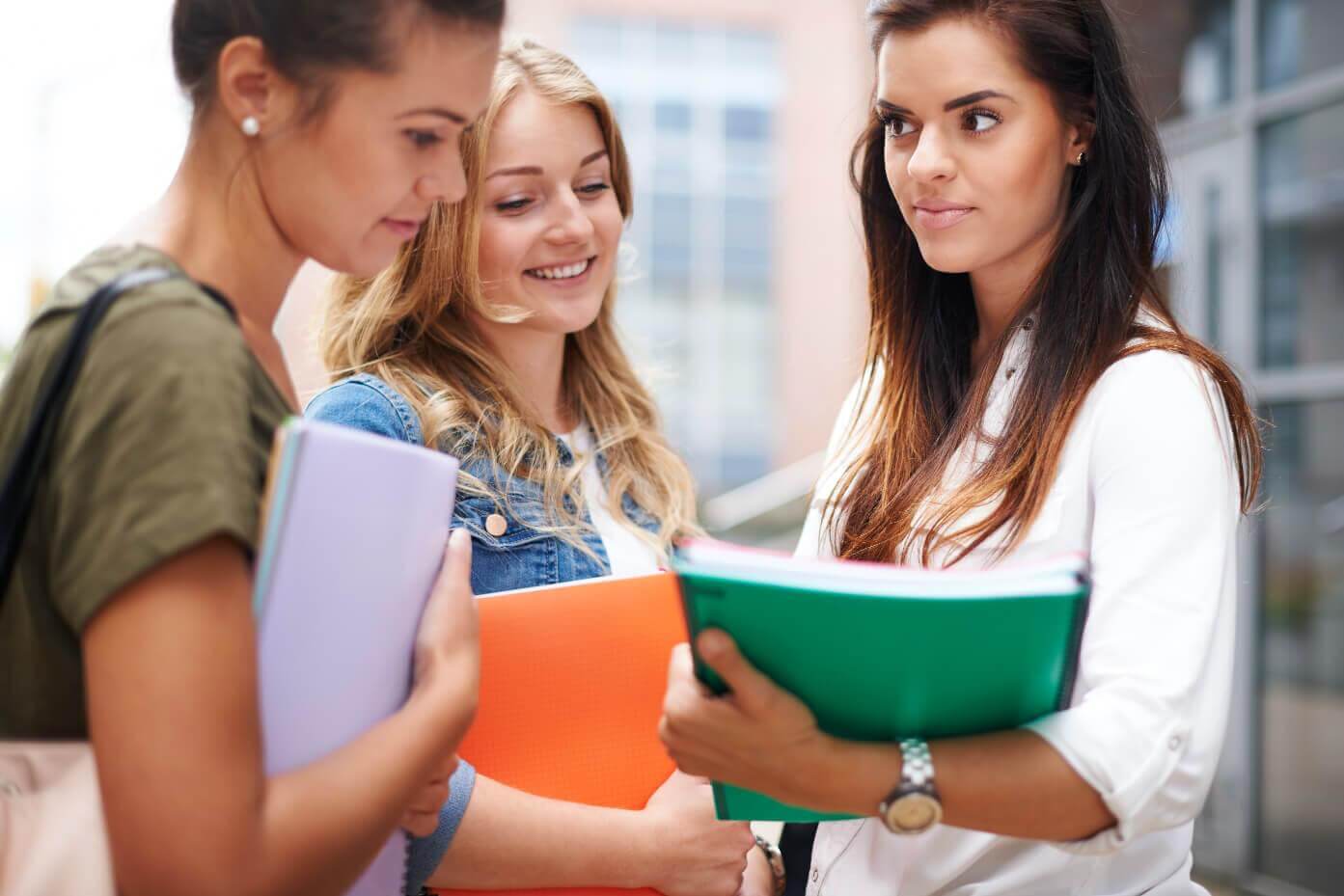
Raising awareness on disability
Materials
1. Introduction
While digital technologies can increase educational inclusion by making information accessible to more people, personalizing learning experiences, and enabling online learning, they might also worsen digital discrimination. Discrimination against people with disabilities is common, and it can have negative consequences for entire communities. Digital platforms and methods that discriminate, whether purposefully or unintentionally, can worsen digital education discrimination.
“The only true disability is the inability to accept and respect differences” (Ryan, 2023)
Recognizing different student viewpoints is critical for developing successful educational strategies that benefit all students (Deepa, Sujatha, & Mohan, 2022). Reducing digital inequalities is vital to increasing educational access and quality to achieve justice and equity (Gottschalk & Weise, 2023).
For a better future, we must work to reduce discrimination and increase disability awareness through platforms for all individuals so that the roots of empathy can emerge and help to break down social boundaries. Disability awareness has gained significance in recent decades, allowing persons with disabilities and society to build empathy for one another. Disability awareness helps reduce society’s conventional thinking, opening many chances for everyone to establish a positive, inclusive society for all. Disability awareness refers to educating society about disability and how individuals may make the required changes (Shigri, 2018).
The successful implementation of disability awareness to foster inclusion and learning opportunities for all students heavily relies on the practical cooperation of all stakeholders, including governments, school administration, teachers and support staff, parents, communities, and others.
Educational campaigns and programs are crucial for raising disability awareness and inclusion. Such initiatives assist in developing curricula and fostering an environment that promotes diversity and caters to the needs of all students, including those with disabilities. Education and awareness-raising are efficient methods for long-term mindset transformation.
This learning unit explains the importance of raising awareness of disability in general, especially in education. The learning unit explores the role of different stakeholders in raising awareness of disability in education towards inclusive education. Furthermore, examples of existing campaigns and programs on disability awareness are discussed.
2. Disability Awareness
Disability awareness is the activity of understanding, acknowledging, and accepting people’s disability-related experiences. Knowing, being aware, and pushing yourself beyond your comfort zone are all required for gaining a greater understanding.
Disability awareness is crucial because it explains how it affects people’s lives and how they can help someone with a disability. It also aids in the elimination of misconceptions regarding impairments and the stigma associated with mental disability. Raising awareness can significantly impact the disabled community’s daily lives. The more individuals who understand the effects of disability, the more accessible resources will become available (Twinkl, 2024).
Disability awareness is a vital step toward ensuring inclusion for persons with disabilities. Often, our worries and discomfort when engaging with persons with disabilities come from a lack of knowledge, uncertainties, and prejudices that might impact our attitudes. It stands to reason that the better informed you are, the more likely you will feel at ease discussing and interacting with someone with a disability at work, in school and training, or in local community (Australian Government Department of Education, 2024).
“The best way to raise awareness and avoid discrimination is for persons with disabilities to be fully included as part of mainstream society, by living in the community, following class in mainstream schools, and being employed in mainstream jobs.” (Dekoninck, 2017)
Figure 1. Normalizing Disability Begins in School | Joseph Schneiderwind | TEDxMSUDenver
Figure 2. General Disability Awareness
Figure 3. Disability Awareness: Intellectual Disability
Figure 4. Disability Awareness: Sensory Disability
Figure 5. Disability Awareness: Physical Disabilit
3. Raising Disability Awareness in Education
Disability awareness in education plays a significant role in shaping the educational landscape. Incorporating knowledge of disability and ableism into regular education benefits students in the long run. It gives students the knowledge and tools they need to respect diversity. These programs aim to foster compassion and empathy by increasing awareness of disabilities. As a result, raising awareness helps to reduce negative attitudes toward people with disabilities.
A recent literature review discovered that legislation, disability and awareness, as well as methods of producing accessible digital learning materials and inclusive digital learning environments, can help in increasing faculty members’ competencies to provide inclusive digital education (Bong & Chen, 2021).
Meaningful inclusion of students with disabilities requires more than simply having students with disabilities in classrooms. Raising all students’ knowledge of disability allows schools to improve the quality of interactions and friendships between students with and without disabilities (Ryan, 2023).
Collaboration between schools, families, and communities is essential for creating inclusive environments for students with disabilities. Good communication among staff is vital for successful inclusive education. Communication with parents is another important aspect of inclusive education. Educational institution managers/school leaders are responsible for providing effective communication and networking opportunities (European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education, 2022).
3.1 The Role of Governments and Ministries
Governments must take adequate action to combat the prejudices that prevent children from attending school by establishing an awareness campaign for parents of disabled children as well as youngsters. Furthermore, they must develop broader awareness campaigns that address discriminatory attitudes in communities, schools, and public service. National governments must (Campaign for Global Education, 2018):
- create appropriate legislative frameworks, and set out ambitious national plans for inclusion,
- provide the capacity, resources, and leadership to implement ambitious national plans on inclusion,
- improve data on disability and education, and build accountability for action,
- make schools and classrooms accessible and relevant for all,
- ensure enough appropriately trained teachers for all,
- challenge attitudes which reinforce and sustain discrimination, and
- create an enabling environment to support inclusive education, including through cross-sectoral policies and strategies that reduce exclusion.
Ministries of Education play a critical role in building the foundation for an inclusive educational landscape by developing educational programs and policies that address the needs of students with disabilities. They play an integral part in ensuring that educational changes incorporate education perspectives and knowledge, promoting an atmosphere in which inclusive education is promoted. Ministries of Education make significant contributions to promoting awareness about the need for inclusion in schools, ensuring that all children, regardless of ability, have access to a high-quality education (Hayes & Bulat, 2017).
3.2 The Role of School Management
School Management upholds laws and regulations that support students with disabilities and ensure they receive the required support and adjustments. They foster an inclusive atmosphere and favorable attitudes toward kids with disabilities by providing regular teacher training. Their leadership is critical to converting schools into places where inclusive education is valued and implemented.
“School principals’ awareness is the key factor in promoting inclusive schools” (Khaleel, Alhosani, & Duyar, 2021)
The primary duties of school management in promoting inclusion are categorized into three categories:
- setting direction,
- human growth, and (3)
- organizational development.
By carrying out these essential functions, school leaders may foster an inclusive school culture in which all students are respected and get a high-quality education (European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education, 2022).
The school managers determine whether to encourage or discourage practices for a more inclusive school. These decisions can also be reflected in a manager’s ability to guarantee that special education teachers collaborate and that general education teachers use peer coaching and other effective tactics. Enhancing the manager’s awareness of the relevance of policies and initiatives in inclusive schools can enhance willingness and ensure successful implementation (Khaleel et al., 2021).
School management must adopt inclusive education values such as integrity, self-awareness, transparency, ethical behavior, democracy, equality, respect, cooperation, acceptance, just and equitable educational opportunities for the success of all students, defense of and respect for diversity as an enriching element, creating a classroom community that values diversity and uses all students’ experiences, and creating accessible and supportive learning environments. Through their leadership, school managers should define and clearly articulate a vision that incorporates inclusive education values, to change their school unit’s habits and practices, as this will inspire and guide their teachers to revise their values and adopt more inclusive ones, reinforcing new understandings of diversity (Vlachou & Tsirantonaki, 2023).
3.3 The Role of Teachers and Supporting Staff
Teachers and supporting staff directly impact the effectiveness of inclusive education by identifying and meeting the needs of students with disabilities. Teachers’ views regarding inclusion and disability can significantly impact the success of integrating students with disabilities into general education classes. Their positive attitudes and proactive interactions with students with disabilities are critical to creating an inclusive classroom environment.
Disability awareness is essential for the professional development of teachers and other educational staff. Educating educators about impairments is crucial for promoting good attitudes and creating an inclusive student environment. Institutions that encourage academic and social inclusion are more likely to cultivate an inclusive environment (Williamson, 2014).
Raising awareness of the importance of inclusive classroom practices is essential, and teacher training and professional development can aid in this process. Pre-service education programs should offer chances for student teachers to interact with and teach children with disabilities and training on the principles and benefits of inclusive education across the curriculum. Professional development may lead to a more favorable attitude towards teamwork among special education teachers and support personnel. (Khaleel et al., 2021).
Teaching disability awareness in schools is not only essential but also necessary for creating a more inclusive and supportive community. Schools may assist students with disabilities in feeling included and supported by introducing disability awareness into curricula, hosting external speakers, and giving teacher and staff training. Simultaneously, students without disabilities learn sensitivity and understanding. Teachers and administrators have critical roles in fostering an inclusive atmosphere, and they must encourage diversity and inclusion (Bukenya, 2023).
3.4 The Role of Parents
Parents play an essential role in advocating for their children’s needs and promoting inclusive education reforms. They contribute to individualizing education by actively participating in their child’s learning and collaborating with teachers. Their engagement in community awareness initiatives raises the profile of inclusive education.
Parents’ perceptions and understanding can also benefit their children, mainly if they are prepared for any expected downsides or challenges their children will face in the inclusive school environment, allowing them to prepare and assist their children mentally and spiritually.
Parents must also collaborate with teachers to establish how to effectively support a student with an impairment outside of the classroom and how to lobby for help to meet the student’s needs. Including parents of disabled children in community initiatives is critical to ensuring that their children receive community support. Awareness-raising efforts should not be restricted to information sharing or sensitization; they should also include opportunities for personal reflection and conversation. (Khaleel et al., 2021).
In recent years, most communication between parents and educators has been via online platforms. This offers certain benefits, such as saving time, but it also presents new obstacles. For example, parents’ options may range, and they may have difficulties accessing the information they seek, especially for parents with disabilities, who may have particular needs while using such systems, contacting the school, or getting information (European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education, 2022).
3.5 The Role of Community
The community’s involvement in educational reforms and transitions contributes to a greater acceptance and understanding of inclusive education. Community members can help break down challenges to inclusion by participating in awareness initiatives and encouraging communication. This collaborative effort ensures that students with disabilities are accepted and thrive in academic and community settings.
To guarantee that all students can access the curriculum in the least restrictive environment, educational professionals must build robust communication channels and processes. Different strategies can be applied, such as (Laud, 2023):
- professional learning communities and co-teaching,
- meetings with families and other professionals (essential for planning and decision-making, highlighting the importance of clear and accessible communication),
- collaborating closely with families (can assists in boosting student development and securing necessary assistance, reinforcing a partnership based on respect, competence, and trust),
- collaboration with experienced teachers and instructional experts can be beneficial especially for those entering the teaching profession in building confidence and skills in inclusive practices.
4. Campaigns and Programs on Disability Awareness in Education
Campaigns to raise awareness of the experiences and rights of people with disabilities may be found worldwide, utilizing various means (Dekoninck, 2017).
Disability awareness programs aim to make schools more accepting and inclusive. Different strategies are utilized, including simulations, group discussions, exposure to relevant literature, real-life interactions, joint projects, and role-playing. These approaches ensure that students have a thorough and compassionate awareness of disability challenges (Williamson, 2014).
In Singapore, a five-year campaign started in 2016 to create a positive and accurate representation of people with disabilities. The program aimed to eliminate stereotypes and improve knowledge of disability and respectful interactions (Disabled People’s Association, 2016).
The 2023 Disability Understanding Campaign, organized by UNNC around the International Day of Persons with Disabilities on December 3rd, aimed to honor the achievements of people with disabilities and raise public understanding and acceptance. The campaign’s topic was collective action to support sustainable development goals for, with, and by people with disabilities, and events will take place from December 1st to December 6th. The campaign invited the entire UNNC community to interact with and learn from persons living with disabilities while also fighting for the removal of barriers and encouraging inclusivity across all types of impairment. (University of Nottingham Ningbo China, 2023).
Every October, the Learning Disabilities Associations of Ontario and LD@school celebrate Learning Disability (LD) Awareness Month. The campaign’s purpose is to raise awareness and remove stigma so that people with learning disabilities can obtain the help they need to attain their full potential (LD@school, 2022).
In 2023, the National Center for Learning Disabilities launched the “Lead with LD” initiative to help de-stigmatize the perception of learning disabilities. The campaign aimed to change people’s attitudes toward learning difficulties and break down stigma. Throughout the month, they shared facts, anecdotes, and words of solidarity to raise awareness and encourage understanding, empathy, and support, as well as put light on the lives of people with learning disabilities (National Center for Learning Disabilities, 2023).
DisabiLily created a thorough list of ideas for disability awareness campaigns that, among others, include (DisabiLily, 2023):
- The Personal Storytelling Campaign shares personal experiences to demonstrate the impact of disability on daily life. The campaign emphasizes the importance of depicting everyday realities, such as problems and the necessity for accessibility.
- The Communication Awareness Campaign promotes inclusive communication strategies such as sign language, captioning, and Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) to empower those with speech and hearing difficulties.
- The Mental Health and Physical Disability Campaign proposes using media to tell authentic stories of people with disabilities and mental health disorders, fostering empathy and challenging misconceptions.
- The Accessible Events Campaign promotes accessibility in public events and offers guidelines to help organizers create inclusive experiences for all attendees.
- The Employment and Disability Campaign strives to remove job barriers for disabled individuals, promote inclusive hiring practices, and emphasize the contributions of disabled people in the workforce.
- The Education and Disability Campaign aims to promote inclusive education policies and provide resources for disabled students and instructors.
- The Accessible Technology Campaign promotes inclusive design and assistive technologies, allowing impaired individuals to participate in the digital world fully.
The Disability Studies program was established at universities such as the University of California, Berkeley, to investigate and educate the social and cultural aspects of disability. The program emphasizes that comprehending disability entails more than simply medical knowledge; it also entails identifying the societal barriers that limit people with diverse physical and neurological problems. Their educational approach promotes diversity and tries to equip future professionals with the understanding required to serve persons with disabilities properly (Rony, 2023).
Vanderbilt University got a major grant to create an advocacy program for students with disabilities and their families. This program seeks to provide students and caregivers with the knowledge and skills to access legal protection and support resources (Somers, 2023).
Furthermore, at Arizona State University, a graduate’s dedication to disability awareness and activism demonstrated the significance of inclusive practices in digital marketing and the potential for higher education to disrupt ableist discourses and practices. A focus on education and advocacy emphasizes the significance of raising awareness, combating prejudices, and ensuring that handicapped voices are heard and considered from the beginning to the end (Chavez, 2023).
Changing Perspectives Curriculum is an online platform with over 180 lesson plans and many resources such as books, films, discussion questions, and experiential activities centered on social-emotional learning, equity, and inclusivity. The mission of Changing Perspectives is to educate, empower, and inspire individuals to become tomorrow’s changemakers by contributing to creating a more inclusive, just, and equitable society (Changing Perspectives, 2023).
5. Conclusion
This text’s comprehensive investigation of disability awareness in education emphasizes the varied approaches required to achieve inclusivity and equity in digital and traditional learning contexts. It emphasizes the critical significance of digital technology in improving educational access while warning against the amplification of digital discrimination. It demonstrates the importance of deliberate design and implementation that accommodates all learners, including those with impairments. The narrative emphasizes recognizing and valuing diversity, not as a threat to prosperity and identity but to enrich communities and improve collective experiences.
The crucial role of many stakeholders in raising disability awareness and adopting inclusive educational practices is central to the conversation. These stakeholders include governments, educational institutions, teachers, support workers, parents, and the larger community. Their collaborative efforts are critical in building environments that recognize and celebrate diversity, ensuring that students with disabilities have equal chances to learn, contribute, and thrive. This collaborative approach is regarded as essential for questioning and changing negative attitudes, stereotypes, and ideas about impairments.
The unit also highlights successful initiatives and programs that have improved disability awareness and inclusivity in educational settings. Using real-life examples and solutions, it provides a roadmap for building curricula and educational climates that cater to all students’ various requirements. These initiatives are beacons of change, highlighting the good consequences of comprehensive awareness-raising efforts and the potential for such undertakings to foster empathy, respect, and understanding across cultural divisions.
Finally, the growth of disability awareness and the pursuit of inclusive education are depicted as ongoing obligations that demand the dedication and involvement of all societal members. By highlighting the importance of empathy, removing obstacles, and celebrating diversity, the material advocates for a future in which education is available to all, free of discrimination or prejudice. This vision for inclusive education is consistent with the larger values of justice, equity, and mutual respect, emphasizing that a truly inclusive society benefits all individuals, not just those with disabilities.
References
Australian Government Department of Education. (2024). Disability Awareness. Retrieved from https://www.adcet.edu.au/our-work/disability-awareness
Bong, W. K., & Chen, W. (2021). Increasing faculty’s competence in digital accessibility for inclusive education: a systematic literature review. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/13603116.2021.1937344
Bukenya, M. (2023). Why Disability Awareness Should be Taught in Schools. Retrieved from https://sperochildinternational.org/why-disability-awareness-should-be-taught-in-schools/
Campaign for Global Education. (2018). Inclusive Education for Children with Disabilities. Handicap International. Retrieved from https://idronline.org/inclusive-education-for-children-with-disabilities-during-covid-19/
Changing Perspectives. (2023). Supporting Disability Awarness. Retrieved from https://changingperspectivesnow.org/disability-awareness/
Chavez, J. De. (2023). How disability awareness, advocacy became a mission for ASU grad. Retrieved from https://news.asu.edu/20231220-how-disability-awareness-advocacy-became-mission-asu-grad
Dekoninck, K. (2017). Awareness raising on the rights of persons with disabilities: Contribution to the council of Eurpoe Strategy on the rights of persons with disabilities, 1–54.
DisabiLily. (2023). 7 Disability Awareness Campaign Ideas. Retrieved from https://disabilily.co.uk/7-disability-awareness-campaign-ideas/
Disabled People’s Association. (2016). ‘See The True Me’ Campaign. Retrieved from https://dpa.org.sg/see-the-true-me-campaign/
European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education. (2022). Inclusive Digital Education.
Gottschalk, F., & Weise, C. (2023). Digital equity and inclusion in education: An overview of practice and policy in OECD countries. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development, (299), 1–73. Retrieved from https://dx.doi.org/10.1787/7cb15030-en
Hayes, A. M., & Bulat, J. (2017). Disabilities Inclusive Education Systems and Policies Guide for Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Research Triangle Park, NC. https://doi.org/10.3768/rtipress.2017.op.0043.1707
Khaleel, N., Alhosani, M., & Duyar, I. (2021). The Role of School Principals in Promoting Inclusive Schools: A Teachers’ Perspective. Frontiers in Education, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2021.603241
Laud, S. (2023). How Collaboration Fosters Effective Inclusion for Special Education Students. Retrieved from https://njalternateroute.rutgers.edu/blog/how-collaboration-fosters-effective-inclusion-special-education-students
LD@school. (2022). Learning Disability Awareness Month. Retrieved from https://www.ldatschool.ca/learning-disability-awareness-month/
National Center for Learning Disabilities. (2023). Lead with LD this LD Awareness Month. Retrieved from https://ncld.org/lead-with-ld-this-ld-awareness-month/
Rony, A. (2023). At 20, Berkeley’s Disability Studies looks ahead with new energy. Retrieved from https://news.berkeley.edu/2023/10/02/evolution-of-disability-studies-at-berkeley
Ryan, M. (2023). DISABILITY AWARENESS IN SCHOOLS. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/disability-awareness-schools-melissa-ryan/
Shigri, N. (2018). The Importance of Disability Awareness: Home and School. Retrieved from https://medium.com/arise-impact/the-importance-of-disability-awareness-home-and-school-eead2276f349
Somers, J. (2023). Burke receives $3 million to develop advocacy program for students with disabilities and families. Retrieved from https://news.vanderbilt.edu/2023/10/05/burke-receives-3-million-to-develop-advocacy-program-for-students-with-disabilities-and-families/
Twinkl. (2024). Spread Awareness of DIsability. Retrieved from https://www.twinkl.si/teaching-wiki/spread-awareness-of-disability
University of Nottingham Ningbo China. (2023). 2023 Disability Awareness Campaign. Retrieved from https://www.nottingham.edu.cn/en/health-and-wellbeing-centre/disability-support-service/2023-disability-awareness-campaign.aspx
Vlachou, A., & Tsirantonaki, S. S. (2023). The Importance of School Principals’ Values towards the Inclusive Education of Disabled Students: Associations between Their Values and Knowledge, Beliefs, Attitudes and Practices. Education Sciences, 13(4), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040360
Williamson, C. (2014). Effects of Disability Awareness Educational Programs on an Effects of Disability Awareness Educational Programs on an Inclusive Classroom Inclusive Classroom Part of the Disability and Equity in Education Commons, Educational Methods Commons, and the Spec. Honors Project, 134, 1–32. Retrieved from https://scholarworks.bgsu.edu/honorsprojects
1. Leadership/ School’s perspective
Inclusive Digital Strategy and Policy for Empowering Inclusive Digital Education
…..
15 min
Understand the importance of raising disability awareness in education. Understand the role of different stakeholders in raising disability awareness in education. Explain appropriate approaches and strategies to promote awareness of individuals with disabilities and their challenges in inclusion in digital education.
Digital discrimination; awareness; raising disability awareness in education








Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can be held responsible for them (2022- 1 -SI01 -KA220-HED-000088368).