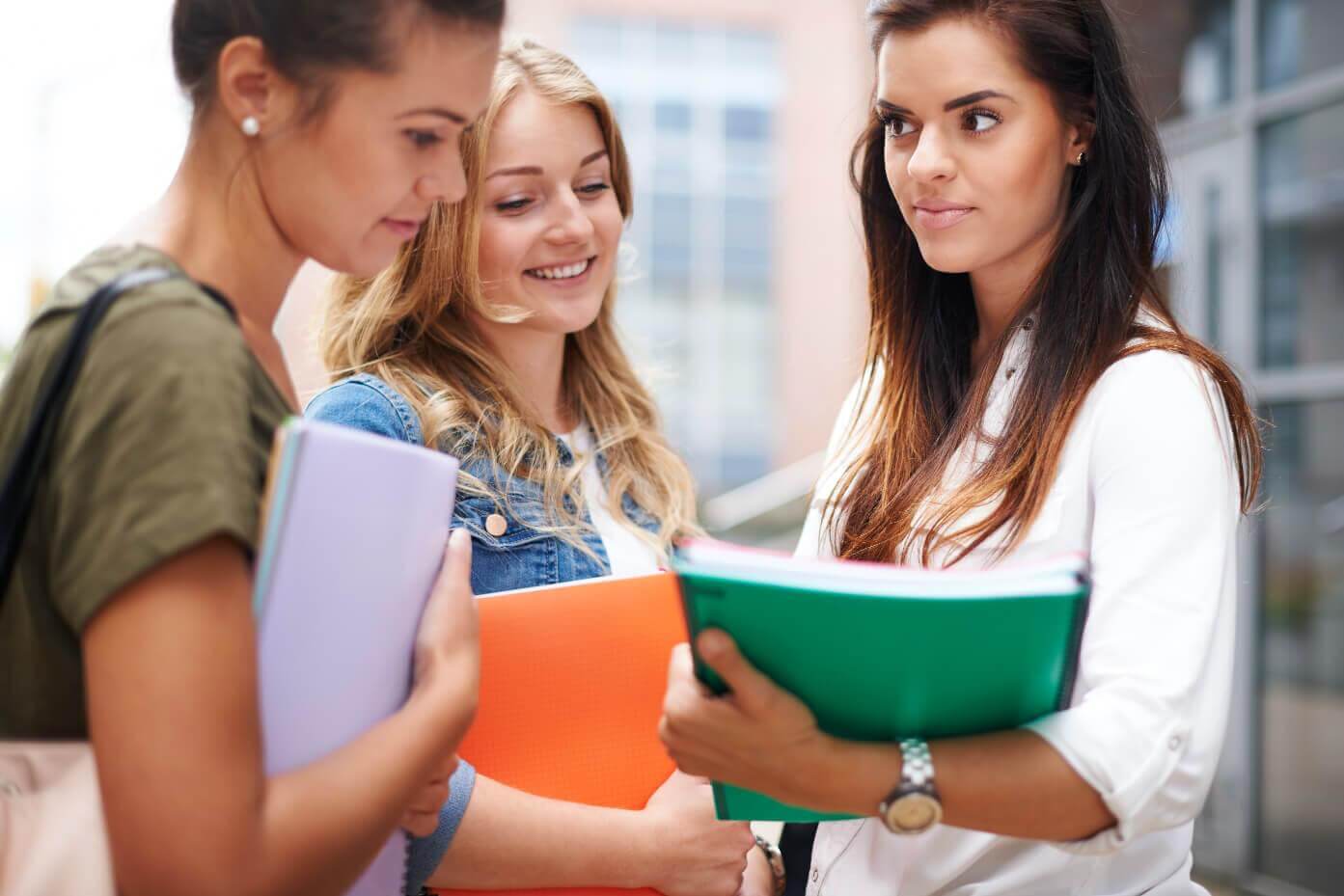
My classroom is inclusive! Part 1
Materials
1. Introduction
Accessibility, defined as the practice of ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, have equal access to opportunities and resources, is a fundamental principle in creating inclusive educational environments. In the context of education, accessibility goes beyond physical accommodations to encompass the provision of accessible materials, technologies, and support services that cater to diverse student needs. It is essential to prioritize accessibility in educational settings to guarantee that every student can fully participate in learning activities and achieve their academic potential. By embracing accessibility, schools can foster a culture of inclusivity, equity, and empowerment that benefits the entire learning community.

2. Definition of Social Inclusion
Social inclusion is a complex concept that encompasses the process of enhancing opportunities and resources for individuals and groups to participate fully in society. It involves improving the terms for people to engage in economic, social, political, and cultural aspects of life (Ekeh and Oladayo, 2013). Social inclusion is characterized by its multidimensional nature, spanning social, political, cultural, and economic dimensions. It operates at various social levels and is influenced by unequal power dynamics in social interactions. This dynamic process impacts individuals differently over time and is closely linked to people’s abilities, opportunities, and dignity, which are distributed unequally among social groups.
2.1. Why Social Inclusion is Necessary
Social inclusion is essential to ensure that all individuals, regardless of their background or specific characteristics such as race, language, culture, gender, disability, social status, or age, can participate fully in society. Groups with unique characteristics are more likely to face challenges like low education levels, unemployment, homelessness, poverty, and social exclusion. A socially inclusive society values all individuals, respects their differences, meets their basic needs, and allows them to live with dignity. By promoting social inclusion, barriers to participation in various aspects of life such as education, employment, leisure activities, and citizenship can be addressed. An inclusive society fosters respect for the identity of all individuals and strives for a balance between the rights and duties of both individuals and society as a whole.
2.2. Multidimensional Measures for Social Inclusion
For example, the multidimensional measures outlined in Law no. 292/2011 in Romania represents a comprehensive approach to addressing social exclusion and promoting active participation in various societal sectors. These measures encompass a wide range of fields including social protection, employment, housing, education, health, information-communication, mobility, security, justice, and culture. By targeting these key areas, the aim is to create an inclusive environment where individuals from all backgrounds can engage fully in economic, social, cultural, and political aspects of society. This approach recognizes the importance of addressing multiple dimensions of social inclusion to ensure that all individuals have equal opportunities to participate and thrive (Ekeh and Oladayo, 2013).
2.3. Creating Inclusive Educational Environments
Establishing inclusive educational environments involves more than just providing accommodations for students with disabilities or special needs. It requires creating a supportive and welcoming atmosphere where all students feel valued and included. This includes not only physical accessibility but also fostering a sense of belonging and acceptance among students. By promoting diversity, equal rights, and community engagement within educational settings, schools can cultivate an environment where every student has the opportunity to learn and grow to their full potential (Amerstorfer and Freijn von Münster-Kistner, 2021).
2.4. Ensuring Accessibility for All
Accessibility is a fundamental aspect of creating inclusive environments in schools. It involves not only physical accessibility but also ensuring that educational materials and resources are accessible to all students, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. This may include providing alternative formats for materials, utilizing assistive technology, and offering appropriate accommodations such as sign language interpreters or visual aids. By prioritizing accessibility in educational settings, schools can ensure that every student has equal access to learning opportunities and can fully participate in academic activities (Starcic, 2010).
2.5. Integrating Educational Technology for Inclusive Teaching
Educational technology plays a crucial role in supporting inclusive teaching practices. By incorporating ICT competencies into the curriculum and providing educators with the necessary tools and training, schools can enhance their ability to cater to diverse student needs effectively. Educational technology can facilitate personalized learning experiences, promote student engagement, and provide opportunities for individualized instruction. By leveraging technology in inclusive classrooms, educators can create dynamic learning environments that support the diverse needs of all students (Starcic, 2010).
2.6. Recommendations for Enhancing Inclusive Education
To further enhance inclusive education practices, it is essential to implement specific recommendations based on research findings. These recommendations may include encouraging parents to place special needs pupils in inclusive schools with government support, ensuring a mix of regular and special education teachers in inclusive classrooms, organizing workshops and training sessions for school administrators and staff to promote best practices in managing inclusive schools effectively. By following these recommendations, schools can improve academic achievement outcomes and create a supportive learning environment that benefits all students (Ekeh and Oladayo, 2013).
3. Case Studies of Accessible Classrooms
Indiana University – Creating Accessible Classrooms
Indiana University provides insights on creating classroom environments that support the success of all students. Strategies include:Alerting students in advance about classroom changes to accommodate various needs.
University of Illinois – eText@Illinois Case Study
The eText@Illinois initiative showcases how browser-based eText enhances accessibility for students through innovative curriculum delivery methods.
Accessing Higher Ground – Teaching Accessibility Case Studies
This session explores curricula components used in computer science, IT, and web courses to teach accessibility topics, emphasizing inclusive education practices.
Galileo Educational Network – Summary of Accessible Classrooms
Galileo researchers highlight successful practices in accessible classrooms, emphasizing media-rich learning environments, Universal Design for Learning principles, and curriculum accessibility for all learners.
Dolphin Computer Access – Accessibility for Inclusive Classrooms
Dolphin Computer Access emphasizes the importance of providing accessible learning materials to cater to diverse learning styles and abilities in modern classrooms. Assistive technology plays a crucial role in enhancing inclusivity by enabling students to access, read, and understand class materials effectively.
These case studies demonstrate various approaches and initiatives implemented by educational institutions to create inclusive and accessible learning environments that cater to the diverse needs of all students.
4. References
Amerstorfer, C. M., & Freiin von Münster-Kistner, C. (2021). Student perceptions of academic engagement and student-teacher relationships in problem-based learning. Frontiers in psychology, 12, 713057.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.713057/full
Ekeh, P. U., & Oladayo, O. T. (2013). Academic achievement of regular and special needs students in inclusive and non-inclusive classroom settings. European Scientific Journal, 9(8).
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/328023570.pdf
Starcic, A. I. (2010). Educational technology for the inclusive classroom. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 9(3), 26-37.
6. Pedagogy: Implementation in the classroom
Inclusive Digital Teaching Practices
Technical support for teachers (PSR 5.7)
10 min
After this unit, you will be able to:
- know the basics of a respectful classroom environment (everyone is made to feel welcome and treated with respect)
- Gain practical knowledge on how to ensure that the learning environment is inclusive toward all users..
respectful classroom environment, inclusive classroom, respect, trust, teaching groups, collaboration, diversity, support








Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can be held responsible for them (2022- 1 -SI01 -KA220-HED-000088368).