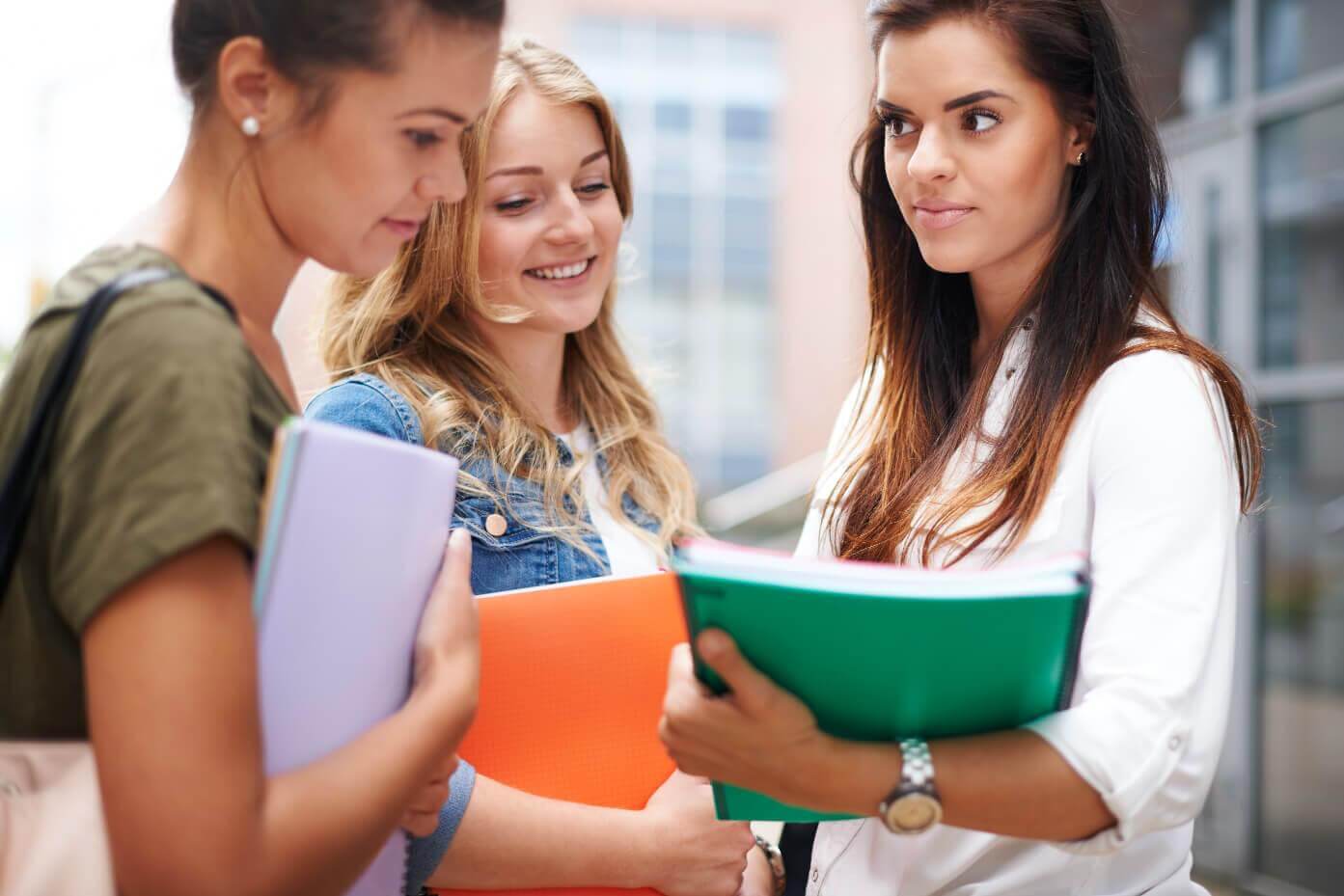
My classroom is inclusive! Part 2
Materials
1. Introduction
We are going to explore the crucial element of putting instructional practices that promote inclusion and respect in the classroom into practice. Creating a welcoming, valued, and respectful atmosphere for every student is not just a goal but also a need for academic success and overall development in today’s diversified educational landscape.
Teachers who want to learn more about how to use digital tools to foster respectful and cooperative learning environments can use this unit as a guide. Through investigating the nexus between pedagogy and technology, educators will unearth useful tactics and cutting-edge resources that can revolutionize their pedagogical approaches and enhance the educational journey for every pupil.
This unit aims to broaden teacher’s pedagogical toolkit, confront their preconceptions, and create learning environments that value diversity and give every student a voice. With cooperation, introspection, and a dedication to ongoing development, it is possible to establish learning environments that enable students to flourish intellectually, socially, and emotionally.
2. Enablers
Assessing the role of digital technologies in Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) to enable collaborative learning groups while promoting diversity involves evaluating several critical factors:
2.1. Accessibility
Accessibility encompasses ensuring that digital tools and platforms utilized in educational settings cater to the diverse needs of all students, regardless of disabilities or varied learning requirements. This involves a thorough examination to verify whether these tools are truly accessible to every student. For instance, assessing the presence of features such as screen readers ensures that visually impaired students can access textual content through audio feedback. Similarly, captioning functionalities are vital for students with hearing impairments, enabling them to comprehend multimedia content effectively. Additionally, adjustable font sizes accommodate students with visual impairments or reading difficulties, enhancing readability and comprehension. By prioritizing these features, educators ensure inclusivity within the learning environment, allowing every student to engage with digital materials and participate actively in the educational process.
2.2. Customization and Personalization
Key elements of contemporary digital learning environments include customization and personalization, which enable teachers to modify their methods of instruction to meet the varied needs of their pupils. It is critical to evaluate digital technologies’ capacity to provide customized learning experiences that accommodate a range of preferences, learning styles, and skill levels. The purpose of this assessment is to determine whether digital tools give students the ability to customize settings and access materials based on their own requirements. For example, depending on their learning styles or aptitudes, pupils could need educational materials in different forms or at different levels of difficulty. To enable individualized learning experiences, look for features like adaptable learning pathways, scalable interfaces, and resource-rich content libraries. Additionally, take into account whether digital platforms have tools that let students monitor their development, create customized learning objectives, and get performance-based feedback. Teachers can create inclusive learning environments where students can interact with content in ways that best suit their individual needs and preferences by giving priority to customization and personalization features in digital technologies. This will increase student autonomy, motivation, and academic success (Pedler, Hudson and Yeigh, 2020).
2.3. Collaboration Features
When considering collaboration features within digital platforms, it’s essential to delve into the specific tools and functionalities that promote interaction and knowledge exchange among students with diverse backgrounds. This evaluation involves examining various collaboration tools, including discussion forums, group chats, and collaborative document editing features. Discussion forums provide virtual spaces for asynchronous discussions, enabling students to engage at their own pace and share ideas on course topics. Group chats offer real-time communication channels where students can engage in synchronous discussions, fostering immediate interaction and collaboration. Collaborative document editing tools allow students to work together on shared documents, presentations, or projects in real time, facilitating collaborative work and enabling students to contribute their unique perspectives and expertise. By assessing how these collaboration features facilitate communication and knowledge sharing among students from different backgrounds, educators can gauge the effectiveness of digital platforms in promoting collaboration and inclusivity within the learning environment.
2.4. Inclusivity
When assessing the inclusivity of digital technologies, it’s vital to examine whether these tools offer equal opportunities for all students to engage in collaborative activities. This evaluation involves considering the extent to which digital platforms support diversity in language, culture, and perspective, ensuring that every student feels empowered to participate fully. Evaluate whether the tools provide features such as multilingual interfaces, translation options, and culturally sensitive content to accommodate diverse backgrounds. Additionally, assess how the platforms encourage the representation and acknowledgment of various viewpoints, fostering an environment where all voices are respected and valued. By prioritizing support for multiple languages, cultural sensitivities, and diverse perspectives, digital technologies can play a pivotal role in promoting inclusivity within collaborative learning environments, ensuring that every student has an equal opportunity to contribute and thrive (Pedler, Hudson and Yeigh, 2020).
2.5. Feedback and Assessment
In assessing whether digital technologies foster inclusivity, it’s essential to examine how these tools provide equitable opportunities for all students to engage in collaborative activities. This evaluation involves considering whether digital platforms support diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds, ensuring that students from various backgrounds can participate fully. Look for features that accommodate multiple languages, such as translation tools or multilingual interfaces, to promote inclusivity and accessibility for all students. Additionally, consider how digital technologies address cultural sensitivities and diverse perspectives, creating an environment where all voices are heard and valued. By prioritizing support for linguistic diversity, cultural sensitivity, and diverse perspectives, educators can ensure that digital technologies promote inclusivity and equity, fostering a collaborative learning environment where every student can actively participate and contribute.
2.6. Training and Support
When evaluating training and support for digital technologies in collaborative learning, it’s crucial to assess the accessibility and adequacy of resources available to both educators and students. Consider the availability of training sessions, workshops, and technical assistance designed to enhance understanding and proficiency in utilizing digital tools effectively. Evaluate the comprehensiveness of these resources in addressing the diverse needs and skill levels of stakeholders, ensuring that all individuals can access the support they require to navigate digital platforms confidently. Additionally, assess the responsiveness of technical assistance channels and the provision of timely support for troubleshooting and addressing issues that may arise during collaborative activities. By prioritizing robust training and support mechanisms, educators can empower both themselves and their students to harness the full potential of digital technologies in collaborative learning endeavors, fostering a more enriching and effective educational experience for all.
2.7. Monitoring and Improvement
Establish mechanisms for monitoring the effectiveness of digital technologies in promoting collaboration and diversity. Collect feedback from students and educators regularly to identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes.
3. Positive behavior
3.1. Consistency across communication channels
Make sure that your conduct is the same in all forms of communication, including digital ones like emails, online forums, and notifications on the learning management system (LMS) as well as face-to-face contacts during lectures and seminars. Regardless of the medium, consistency reinforces the expectation of polite behavior (Browne, 2013).
3.2. Professional and courteous language
Exhibit civility and professionalism in all written and spoken correspondence with kids. When sending emails or sending messages online, use formal language and tone. Be sure to address students by their preferred titles and names. Steer clear of insulting words, sarcasm, and any communication that can be interpreted as disrespectful.
3.3. Active listening and empathy
Engage in active listening whenever you communicate with students, whether in online forums or in-person conversations. Respond to the inquiries, worries, and viewpoints of the pupils with compassion and understanding. Even if you don’t agree with what the students have to say, respect and acknowledge their contributions (Browne, 2013).
3.4. Encourage constructive feedback
Encourage the creation of an atmosphere where helpful criticism is valued and appreciated. Set a positive example for others by giving constructive criticism that is focused on particular actions or behaviors rather than personal traits. In a similar vein, exhibit how to accept criticism well and turn it into a chance for development.
3.5. Promote inclusivity and diversity
Interact with students in a way that celebrates variety and exemplifies inclusivity. provide students’ diverse origins, experiences, and points of view recognition and appreciation, and provide them opportunities to have their voices heard. Avoid saying or doing anything that can be interpreted as marginalizing or excluding any student group.
3.6. Transparency and accountability
Be open and honest about your choices, expectations, and behavior online as well as in person. Explain the reasoning behind the teaching strategies, grading standards, and course policies in detail. Accept responsibility for any errors or misunderstandings and show that you are an accountable person by taking immediate, appropriate action to rectify them.
3.7. Create a supportive learning community
Encourage children to feel supported and a part of the group by setting an example of cooperation and teamwork. Students should be encouraged to collaborate, exchange resources, and support one another’s success. Respect the time, work, and contributions of your students. Provide chances for peer mentoring and teamwork (Browne, 2013).
3.8. Continuous reflection and improvement
Reflect on and assess your own actions and communication styles on a regular basis. Get student input on your communication style and method of instruction, then utilize this input to pinpoint areas that need work. Dedicated to your continued professional development and development as an instructor.
4. Digital spaces
Creating collaborative digital spaces involves leveraging various online platforms and tools to foster meaningful interactions and collaboration among students. Here’s an expanded version of how you can achieve this (Yarbro et al., 2016):
4.1. Selecting appropriate digital platforms
Select digital platforms like online discussion boards, online forums, collaborative document editing tools like Google Docs, or video conferencing apps like Zoom and Microsoft Teams that encourage participation and cooperation. Choose the platforms that most closely match your course’s requirements and learning objectives by carefully weighing their features and functions.
4.2. Setting up online discussion forums
Establish online message boards or discussion forums where students can participate in asynchronous discussions about the assignments, projects, and course subjects. Students should be encouraged to actively participate by posing queries, offering their opinions, and politely and constructively reacting to the contributions of their peers (Yarbro et al., 2016).
4.3. Facilitating group work
Make use of digital channels to encourage student collaboration and group projects. Assign group tasks or exercises where students must cooperate to accomplish shared objectives. Establish policies and make available tools (such document repositories, communication protocols, and project management software) to facilitate productive teamwork.
4.4. Encouraging peer feedback and review
Encourage peer evaluation and feedback as a means of fostering teamwork. Students should be encouraged to provide their peers helpful criticism on their unfinished projects, drafts of essays, or presentations. Make use of digital platforms to streamline peer review procedures so that students can communicate online and share edits and feedback (Yarbro et al., 2016).
4.5. Promoting inclusive collaboration
Encourage a collaborative, equitable, and inclusive atmosphere where all students are treated with respect and feel appreciated. Give students the chance to contribute and exchange ideas by giving them the chance to talk about their views, experiences, and cultural backgrounds (Yarbro et al., 2016).
4.6. Monitoring and moderating online interactions
Keep an eye on conversations and exchanges on the internet to make sure they stay civil and useful. As necessary, step in to resolve any disputes that may emerge or disruptive behavior or improper content. To keep a welcoming and constructive online community, establish rules for behavior and communication, then consistently enforce them (Yarbro et al., 2016).
4.7. Reflecting on collaborative experiences
Urge pupils to consider their experiences working together and to note any lessons they may have learnt. Encourage them to think about the benefits and drawbacks of collaborating in virtual environments, as well as methods for removing obstacles and enhancing future teamwork. To emphasize the value of teamwork and how it affects learning outcomes, use reflection exercises.
5. Student engagement
Providing opportunities for student voice and choice is essential for fostering student engagement, ownership of learning, and a sense of agency in the educational process. Here’s an expanded look at how you can empower students to have a voice in their learning using digital technologies (Carter and Darling-Hammond, 2016):
5.1. Incorporate diverse learning activities
Provide a range of educational activities that accommodate various interests, preferences, and learning styles. Provide students flexibility and choice in how they interact with the course material by utilizing digital technology. Some examples of this include giving them choices for interactive simulations, multimedia resources, and reading materials.
5.2. Encourage student reflection and self-assessment
Include reflection exercises in your course that help students consider their goals, learning outcomes, and development. Encourage self-evaluation and self-directed learning by utilizing digital resources like blogs, journals, or online discussion forum reflection prompts.
5.3. Facilitate peer collaboration and feedback
Give pupils the chance to work together with their classmates and give each other feedback on their projects. For peer review exercises, group projects, or collaborative document editing, use digital platforms so that students can exchange ideas, offer helpful critique, and gain insight from one another’s viewpoints.
5.4. Implement surveys and polls
Collect student opinions on the course’s content, delivery style, and evaluation techniques by using digital survey tools. Use student feedback to guide your instructional decisions by asking them to be frank and constructive about what they think is going well and what may be improved.
5.5. Create discussion forums and online communities
Create social media groups or online discussion forums where students may participate in conversations, pose questions, and exchange resources about the subjects covered in the course. Urge students to take an active role in these virtual communities by asking insightful questions, contributing their own ideas, and answering those of their peers (Pedler, Hudson and Yeigh, 2020).
5.6. Offer choice in assignments and assessments
Give pupils the chance to demonstrate what they have learned using a range of flexible and creative evaluation techniques. Provide students with e-portfolios, digital storytelling projects, multimedia presentations, and project-based assessments that are in line with their interests and strengths by utilizing digital technology.
5.7. Personalize learning pathways
Personalized learning pathways allow you to adjust the learning process to each student’s unique needs and preferences. Utilize learning management systems or digital adaptive learning platforms with configurable features to offer activities, assessments, and content that are tailored to each student’s learning profile and progress (Carter and Darling-Hammond, 2016).
5.8. Promote student leadership and advocacy
Give students the tools they need to take charge of their education and speak up for their own interests and needs. Give students the chance to take the lead in leading collaborative learning efforts by encouraging them to suggest ideas for projects, activities, or study topics (Pedler, Hudson and Yeigh, 2020).
6. Conclusion
Finally, this unit has given participants a road map for fostering respectful and inclusive learning environments in the classroom by carefully integrating digital technology and pedagogy. Teachers have received important insights into the fundamentals of inclusive pedagogy and the role of digital tools in facilitating collaborative learning experiences by actively participating in the material and investigating useful solutions.
It is evident from our reflections on this unit’s journey that cultivating inclusivity and respect calls for focus, purposeful effort, and a dedication to continuous improvement. Through the use of these tactics and the utilization of the available digital tools, educators may establish transformative learning environments in which each student experiences a sense of empowerment, support, and value.
As we move forward, let’s not waver in our commitment to building inclusive schools that value diversity, encourage teamwork, and foster an environment of empathy and respect. Together, as a community of educators, we can motivate positive change and establish learning environments that pave the way for both lifetime achievement and academic excellence.
7. References
Browne, K. A. T. E. (2013). Challenging behaviour in secondary school students: Classroom strategies for increasing positive behaviour. Teachers’ Work, 10(1), 125-147.
https://ojs.aut.ac.nz/teachers-work/article/view/576
Carter, P., & Darling-Hammond, L. (2016). Teaching diverse learners. Handbook of research on teaching, 5, 593-638.
https://www.torrossa.com/gs/resourceProxy?an=5328173&publisher=FZT653#page=606
Pedler, M., Hudson, S., & Yeigh, T. (2020). The teachers’ role in student engagement: A review. Australian Journal of Teacher Education (Online), 45(3), 48-62.
https://search.informit.org/doi/abs/10.3316/ielapa.270830255864389
Yarbro, J., McKnight, K., Elliott, S., Kurz, A., & Wardlow, L. (2016). Digital instructional strategies and their role in classroom learning. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 48(4), 274-289.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15391523.2016.1212632
6. Pedagogy: Implementation in the classroom
Inclusive Digital Teaching Practices
Technical support for teachers (PSR 5.7)
10 min
After this unit, you will be able to:
- define how digital technologies support a safe and trustful educational environment
respectful classroom environment, inclusive classroom, respect, trust,
teaching groups, collaboration, diversity, support, cybersecurity,
fishing








Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can be held responsible for them (2022- 1 -SI01 -KA220-HED-000088368).