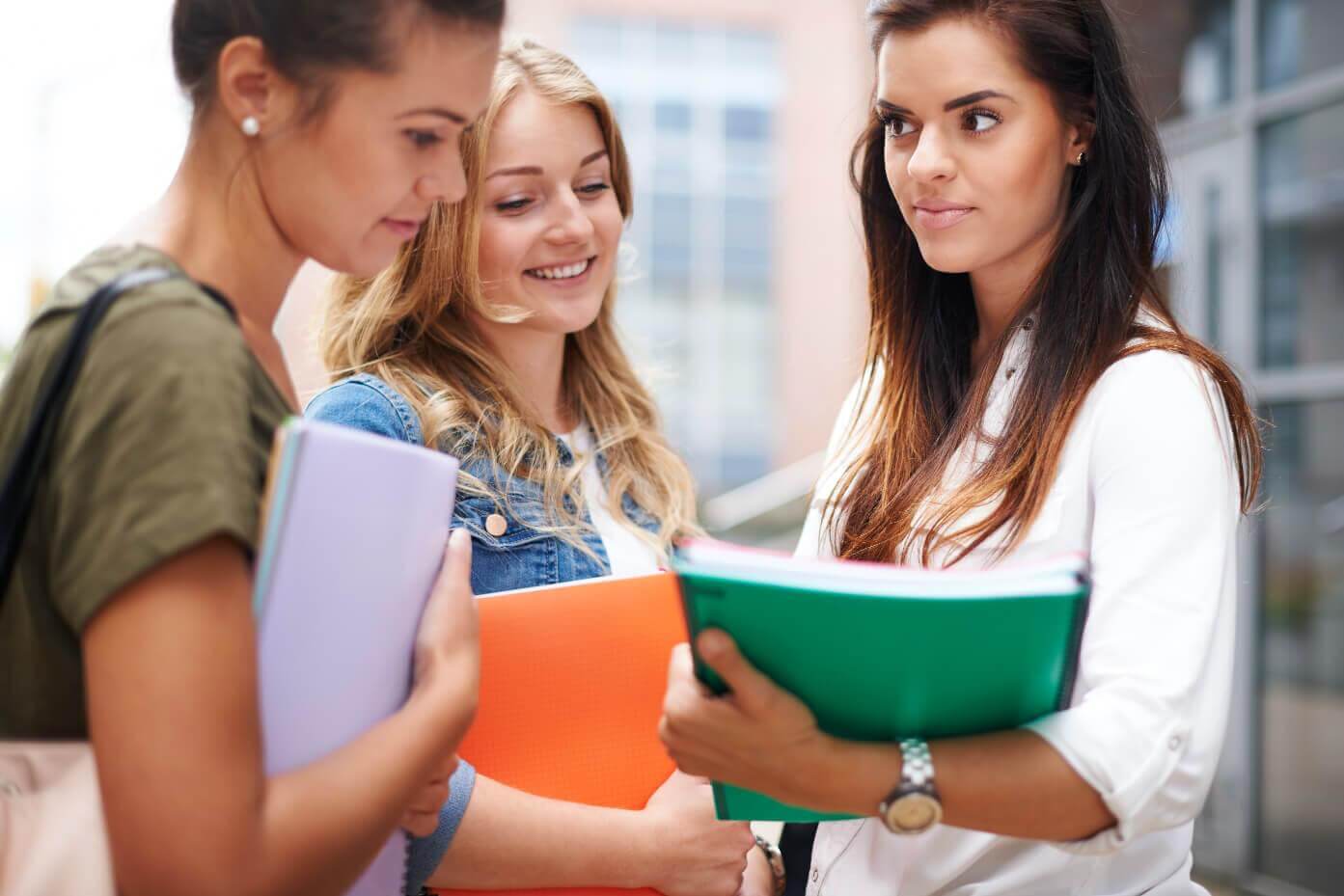
Who is in my classroom?
Materials
1. Introduction
Effective learning outcomes in today’s diverse educational environment are largely dependent on creating a respectful and inclusive classroom atmosphere. This essay examines the value of inclusive classroom cooperation as well as methods for fostering a respectful environment in learning environments.
Beyond simple diversity, inclusive classroom collaboration actively fosters equity and a sense of belonging for every student, regardless of their identities, experiences, or skills. It is an example of a transformative strategy that highlights the importance of each student’s distinct contributions and viewpoints within the community of learners.
Fundamentally, inclusive classroom collaboration acknowledges the diverse range of experiences, aptitudes, and knowledge that every student offers to the learning environment. It recognizes variances in learning styles, cognitive capacities, and cultural backgrounds in addition to obvious distinctions like race, ethnicity, gender, and financial level.
There are several ways that educators can use to promote inclusive classroom collaboration. Students might collaborate to achieve a common goal through group projects and activities, for example, which promotes collaboration and an understanding towards different viewpoints. Peer-to-peer learning experiences that foster inclusivity and intellectual understanding include cooperative learning exercises and peer tutoring.Fundamentally, inclusive classroom collaboration acknowledges the diverse range of experiences, aptitudes, and knowledge that every student offers to the learning environment.
Furthermore, adaptable grouping techniques let students work with classmates who have different experiences and skill levels, which promotes empathy and cross-cultural understanding. Encouraging student voice and choice in the classroom gives students the confidence to express their thoughts, passions, and experiences, which improves their feeling of identity and ownership over their education.
Establishing a polite atmosphere is crucial for encouraging diversity and making sure that every student feels appreciated and supported, in addition to encouraging collaboration. In addition to actively listening, empathetically interacting with children, and maintaining an open mind, educators are vital role models for all pupils (Anis, 2023).
Teachers may foster an inclusive and respectful environment in the classroom by addressing bias, discrimination, and microaggressions through open communication and education. Fostering respect and advancing inclusivity requires creating a secure and encouraging learning environment in the classroom where students may express themselves freely without worrying about prejudice or judgment.
In summary, encouraging effective learning outcomes and fostering a positive learning environment for all students depend heavily on inclusive classroom cooperation and fostering a respectful environment. Teachers can establish inclusive learning environments where every student feels respected, supported, and encouraged to succeed by putting collaboration and respect-building tactics into practice.
2. Understanding Inclusive Classroom Collaboration:
In an inclusive classroom, collaboration permeates every aspect of instruction, interaction, and assessment. Students engage in cooperative activities, group projects, and peer-to-peer discussions that foster meaningful interactions and promote collective problem-solving. Through these collaborative learning experiences, students develop essential skills such as communication, teamwork, critical thinking, and empathy.
Central to inclusive classroom collaboration is the notion of respect for diversity and inclusivity. Students are encouraged to recognize and appreciate the unique perspectives, backgrounds, and contributions of their peers, fostering a culture of mutual respect and understanding. By creating a supportive and inclusive learning environment where all voices are valued and heard, teachers cultivate a sense of belongingness and empowerment among students.
Inclusive classroom collaboration extends beyond the confines of the classroom, encompassing partnerships with families, communities, and other educational stakeholders. By forging meaningful connections with diverse communities and leveraging their resources and expertise, educators can create more inclusive and culturally responsive learning environments.
Achieving inclusive classroom collaboration requires intentional efforts to dismantle barriers to participation and create opportunities for all students to thrive. This may involve adopting flexible instructional strategies, providing accommodations and support services, and promoting culturally relevant and responsive pedagogies. It also entails fostering a culture of openness, empathy, and respect, where differences are celebrated as strengths rather than viewed as deficits (Anis, 2023).
Ultimately, inclusive classroom collaboration holds the promise of not only enhancing academic outcomes but also fostering a more equitable, inclusive, and just society. By embracing diversity, equity, and inclusivity as core principles of education, educators can create transformative learning experiences that empower all students to reach their full potential and contribute positively to their communities and the world.
3. Promoting Inclusive Classroom Collaboration:
3.1. Differentiated Instruction:
Differentiated Instruction is a pedagogical approach that recognizes the diversity among learners and seeks to accommodate these differences through personalized teaching strategies. At its core, it acknowledges that students come to the classroom with varying backgrounds, abilities, interests, and learning styles. By implementing differentiated instruction strategies, educators can effectively cater to the unique needs of each student, fostering a more inclusive and supportive learning environment (Tomlinson, 2014).
One key aspect of differentiated instruction is the recognition that no two students learn in exactly the same way. Some students may excel in visual learning environments, while others may thrive with hands-on activities or auditory instruction. By offering a variety of instructional methods and materials, teachers can engage students across different modalities, ensuring that all learners have opportunities to succeed (Rasooli, et al., 2021).
Moreover, differentiated instruction allows teachers to provide appropriate levels of challenge for students at different readiness levels. For example, advanced learners may benefit from enrichment activities or accelerated pacing, while struggling learners may require additional support and scaffolding to grasp essential concepts. By tailoring instruction to meet students where they are academically, educators can promote growth and success for all learners (Tomlinson, 2014).
Furthermore, differentiated instruction promotes a culture of inclusivity and equity in the classroom. By recognizing and valuing each student’s unique background, experiences, and abilities, teachers create an environment where every student feels respected and supported. This sense of belonging is essential for fostering positive academic outcomes and promoting student engagement and motivation.
In essence, differentiated instruction is about honoring the diversity of learners and providing tailored support to meet their individual needs. By embracing this approach, educators can create dynamic and inclusive learning environments where every student has the opportunity to thrive and reach their full potential.
3.2. Group Work and Cooperative Learning
One of the most effective ways to promote student collaboration in the classroom is to reward group work and cooperative learning activities. Teachers foster peer connection and the development of critical communication skills and mutual respect in their pupils by offering projects that require teamwork.
By participating in cooperative learning, students can develop their capacity to work as a team by having opportunities to collaborate with their peers. This cooperative effort builds a sense of community in the classroom in addition to improving the learning process.
Additionally, cooperative learning enables students to gain from the special talents and viewpoints of one another. Students acquire a more profound comprehension of the subject matter by utilizing the varied abilities and experiences of their classmates.
Cooperative learning activities can promote students’ active participation and engagement as they collaborate to accomplish shared objectives. This cooperative learning strategy encourages students to feel empowered to share their thoughts and opinions in a supportive learning environment, giving them a sense of ownership over their education.
Fundamentally, integrating cooperative learning activities and group work into the classroom fosters student participation while also developing critical abilities like respect, communication, and teamwork. By adopting these techniques, teachers may establish vibrant, welcoming classrooms where each student has the chance to grow and flourish.
4. Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
The ideas of Universal Design for Learning (UDL) advocate for the development of curricula and instructional materials that are accessible to all students, regardless of their varied learning needs and skills. UDL represents a paradigm change in education. Fundamentally, UDL acknowledges that learners have different interests, strengths, and challenges, and it aims to offer a variety of learning pathways in order to successfully accommodate this diversity (Estes, Beverly, and Castillo, 2020).
Using multiple forms of representation is one of the main principles of Universal Design of Learning (UDL). Teachers can accommodate diverse learning styles and preferences by delivering material in a variety of media, including text, images, videos, and audio. By ensuring that every student has access to the material in a way that speaks to them, this strategy fosters understanding and engagement (Estes, Beverly, and Castillo, 2020).
Furthermore, UDL highlights how crucial it is to offer a variety of interaction opportunities to boost students’ motivation and enthusiasm in their studies. Teachers can accomplish this by giving students freedom and choice in their assignments, including them in engaging and practical activities, and leveraging their passions and interests. Teachers can develop intrinsic motivation in their students and encourage active participation in the learning process by making the material relevant and meaningful to the pupils.
Furthermore, UDL promotes the availability of many modes of expression, enabling students to exhibit their comprehension and expertise in various manners. Options for written assignments, oral presentations, multimedia projects, and practical demonstrations may be included in this. Teachers may respect each student’s unique preferences and strengths by offering flexible assessment possibilities, which encourage self-expression and creativity (Rasooli, et al., 2021) .
Teachers may break down barriers to learning and provide inclusive learning environments where every student has an equal chance to achieve by putting UDL concepts into practice. UDL acknowledges and celebrates the diversity of learners, enabling them to access and interact with the curriculum in ways that best suit their unique needs and talents, as opposed to requiring them to conform to a one-size-fits-all approach.
By accepting variety and offering flexibility in curriculum design and training, UDL essentially fosters inclusivity. A dynamic and responsive learning environment where each student can flourish and realize their full potential can be created by educators by embracing diverse forms of representation, interaction, and expression (for further information see Fostering Equal Value in HEI Classrooms)
5. Creating a Respectful Environment
A respectful environment is characterized by mutual understanding, empathy, and appreciation for diversity. It is essential for fostering positive relationships among students and between students and teachers. In a respectful environment, students feel safe to express their thoughts and opinions, knowing that they will be heard and respected.
Strategies for Cultivating a Respectful Environment:
5.1. Establishing Clear Expectations
clear expectations for behavior and communication helps create a respectful classroom culture. Teachers should articulate guidelines for respectful interactions and model positive behavior themselves. Consistency in enforcing expectations reinforces the importance of mutual respect and creates a conducive learning environment (Tomlinson, 2014) (Rasooli, et al., 2021).
5.2. Promoting Active Listening
Active listening is a fundamental aspect of respectful communication. Teachers can encourage active listening by providing opportunities for students to share their perspectives and actively engaging with their contributions. By demonstrating attentive listening skills, teachers set a positive example for students and foster a culture of respect (Bond and Bedenlier, 2019).
5.3. Addressing Bias and Stereotypes:
Addressing bias and stereotypes is crucial for promoting respect and inclusivity. Teachers should facilitate discussions about diversity, equity, and social justice, encouraging students to critically examine their own biases and assumptions. By fostering awareness and understanding of different perspectives, teachers can promote empathy and respect for all individuals.
6. Conclusion:
Building a respectful and inclusive classroom community is essential to effective teaching and learning. A rich educational experience that benefits every student is made possible when educators give priority to these elements. Let’s explore the tactics that teachers can use to build respect and encourage teamwork, which will eventually result in inclusive classrooms where all students succeed. In order to foster a collaborative culture, it is first necessary to provide opportunities for students to collaborate, share ideas, and gain knowledge from one another. Group projects, peer-to-peer conversations, and cooperative learning exercises can help achieve this. Teachers that promote collaboration help to build a sense of community in the classroom as well as information exchange (Bond and Bedenlier, 2019).
Finally, educators ought to show by their words and deeds that they genuinely care about diversity and respect. In order to consistently improve their teaching methods, this entails actively seeking more student feedback, demonstrating inclusive conduct, and pushing for equity. Ultimately, teachers who prioritize inclusive classroom cooperation and respect not only improve the learning environment but also help to shape the future generation of socially conscious, compassionate people who can thrive in a diverse and interconnected society. Teachers are vital in creating a more just and inclusive society for future generations because of their commitment to inclusivity and respect.
7. References
Anis, M. (2023). Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Inclusive English Language Teaching: Strategies and Implications for Learner Diversity. Journal of Multidisciplinary Educational Research, 12(6).
http://ijmer.s3.amazonaws.com/pdf/volume12/volume12-issue6(5)/9.pdf
Bond, M., & Bedenlier, S. (2019). Facilitating student engagement through educational technology: towards a conceptual framework. Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 2019(1).
https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1228555
Estes, M. D., Beverly, C. L., & Castillo, M. (2020). Designing for accessibility: the intersection of instructional design and disability. Handbook of Research in Educational Communications and Technology: Learning Design, 205-227.
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-36119-8_8
Rasooli, A., Razmjoee, M., Cumming, J., Dickson, E., & Webster, A. (2021). Conceptualizing a fairness framework for assessment adjusted practices for students with disability: An empirical study. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 28(3), 301-321.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0969594X.2021.1932736
Tomlinson, C. A. (2014). The differentiated classroom: Responding to the needs of all learners. Ascd.
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/016235320302700203
6. Pedagogy: Implementation in the classroom
Inclusive Digital Teaching Practices
Technical support for teachers (PSR 5.7)
10 min
After this unit, you will be able to:
- know the basics of a respectful classroom environment (everyone is made to feel welcome and treated with respect) and identify some digital tools so that all students feel equally valued and mutually respects
- facilitate the organization of teaching groups by digital technologies in which students can collaborate by valuing the diversity of each one
respectful classroom environment, inclusive classroom, respect, trust, teaching groups, collaboration, diversity, support








Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can be held responsible for them (2022- 1 -SI01 -KA220-HED-000088368).